Brazil’s indigenous peoples, already targeted by loggers, face a powerful foe in the new president. We must protect them!

Οn 1 January, Jair Bolsonaro will be sworn in as Brazil’s 38th president. He has expressed open disdain for the indigenous peoples of Brazil, and it is no exaggeration to say that some of the world’s most unique and diverse tribes are facing annihilation. Genocide is defined by the UN as “the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group”. Large-scale mass genocides rightly receive global attention, yet countless others go unreported and unpunished because the victims number only a few hundred, or even a few dozen.
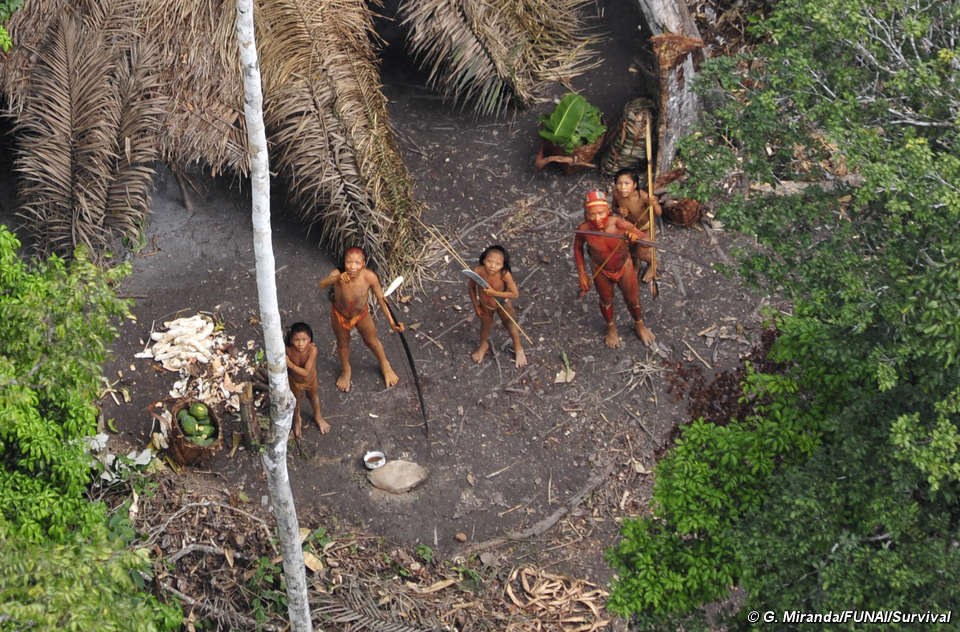
Right now, deep in the Amazon rainforest, a small tribe of survivors is on the run. They are the Kawahiva, an uncontacted tribe of just a few dozen people, the victims of waves of horrific attacks which have pushed them to the brink of extinction. We know almost nothing about them, except that they are fleeing chainsaws in a region with the highest rate of deforestation in the Amazon. Brazil’s first ever investigation into the genocide of an uncontacted tribe was launched in 2005, and 29 people suspected of involvement in killing Kawahiva were detained but later released, including a former state governor and a senior policeman. The case stalled for lack of evidence.
The Kawahiva’s territory lies near the town of Colniza, one of the most violent areas in Brazil, where 90% of income is from illegal logging. Survival International, the global movement fighting for the rights of tribal people, has recently called for increased police protection for the team responsible for protecting the Kawahiva’s land. FUNAI, Brazil’s Indian Affairs Department, has been prevented from properly carrying out its work in the area due to violence from illegal loggers and ranchers, leaving the tribe exposed.
Preventing a genocide of uncontacted people is not a priority for Bolsonaro. He once said: “There is no indigenous territory where there aren’t minerals. Gold, tin and magnesium are in these lands, especially in the Amazon, the richest area in the world. I’m not getting into this nonsense of defending land for Indians.”
Indigenous peoples are frequently regarded as obstacles to the advance of agribusiness, extractive industries, roads and dams. As more rainforest is invaded and destroyed in the name of economic “progress” and personal profit, uncontacted tribes become targets – massacred over resources because greedy outsiders know they can literally get away with murder. These are silent, invisible genocides, with few if any witnesses. The news often only emerges months, if not years, later.

The UN convention on genocide came into force 70 years ago, yet entire tribes continue to be exterminated by the dominant society in order to steal their land and resources. Symbolic of this is the “last of his tribe”, a lone man living in a patch of forest in Brazil’s western Amazon region. We know nothing about him except that he rejects all contact, and survived waves of attacks carried out in the 1970s and 80s against his people and his neighbours, the Akuntsu tribe – of whom just four survive. No one has ever been prosecuted for these genocides. This impervious mentality harks back to the wild west of the 18th and 19th centuries, when Native Americans in the US were slaughtered by the colonists. Indeed, Bolsonaro himself has declared: “It’s a shame that the Brazilian cavalry wasn’t as efficient as the Americans, who exterminated the Indians.”
The majority of the world’s 100 or so uncontacted tribes live in the Brazilian Amazon. They are aware of the outside world, use and adapt outside goods for their own purposes and may engage sporadically with contacted tribes nearby. Their hunter-gatherer lifestyles require vast and acute botanical and zoological knowledge. With this unique understanding of sustainable living, they protect some of the largest and most biodiverse forests on Earth.
Uncontacted people make homes, love their families, tend the landscape, and, like any of us, want to live well and in peace. Where their rights are respected they continue to thrive, but all face catastrophe unless their land is protected.
The largest area of primary rainforest under indigenous control is the Yanomami territory, which straddles part of the Brazilian border with Venezuela. It is home to around 32,000 Yanomami, including some groups who are uncontacted. A “epidemic” of goldminers have illegally invaded the territory to pillage its riches, bringing disease and death to the tribe.
In May, Yanomami reported that two uncontacted members of the tribe had been murdered by miners. FUNAI had closed its protection post in the area due to a lack of funds and, while prosecutors have ordered the post to be reopened, the authorities have not yet investigated the killings.
Bolsonaro opposed the creation of the Yanomami territory in the 1980s, calling it a “crime against the motherland”, and a “scandal”. He affirmed his beliefs in 2017, saying he regarded the creation of the reserve as “high treason”, and there are murmurs that this is an area already in the crosshairs of the new administration.

Bolsonaro intends to take FUNAI out of the justice ministry and into a newly created ministry for women, family and human rights. This is a move sure to weaken the department’s efficacy and clout – it has already been undermined by huge budget cuts. Bolsonaro has appointed Damares Alves as the new minister, an evangelical preacher and congressional aide who co-founded Atini, a controversial group that evangelises in indigenous communities and is subject to an investigation by public prosecutors for inciting racial hatred against indigenous peoples.